Hi all,
Below are the private/public funding distribution in Korea, Japan. Based on the data from OECD, Japan has a higher and stable public funding ratio, and public funding in Korea is catching up. For China, the detailed breakdown indicates that public funding is also increasing rather fast.
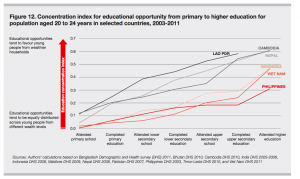
These findings coincide the observations in public expenditure per HE student (2000 vs. 2011) and in public expenditure on HE as a percentage of total public education expenditure. At the right hand sides of the axis, we can tell that from 2000 to 2011, Korea, Japan and China have all increased public expenditure on HE. This is not the case of many other Asian countries.
Interestingly Japan and Korea have a higher proportion of gross domestic expenditure on R&D than China. For private enrollment and Institutional Share in HE, Korea is the highest across all Asian countries, Japan more or less similar and China lagging far behind.
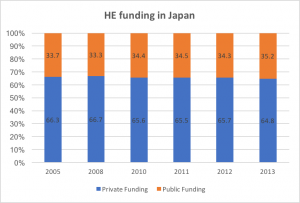
Source: OECD
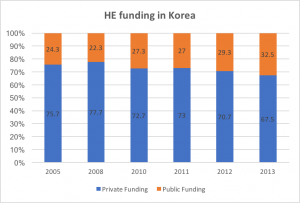
Source: OECD
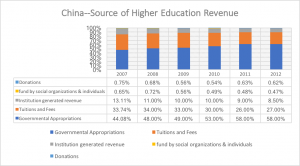
Source: China Statistical Yearbook 2015
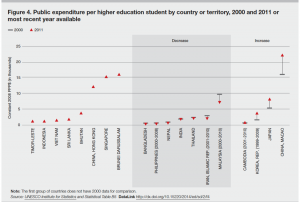
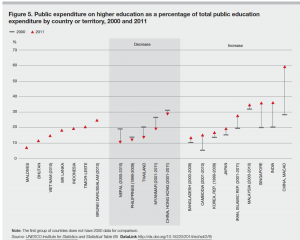
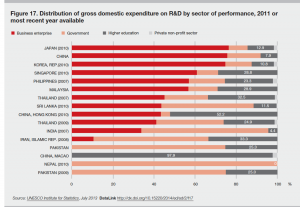
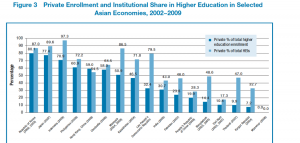
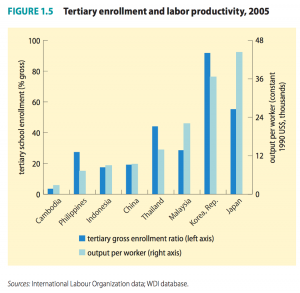
Source: Asian Development Bank