A DNA biosensor is a sensing device that converts the presence of a target DNA into a detectable electrical signal. It consists of two parts, one is the identification component, the DNA probe, and the other is the transducer. The protagonist of the recognition component is used to sense whether the sample contains the target DNA to be tested; the transducer converts the signal perceived by the recognition component to observe the recorded signal. Usually, a single-stranded DNA is solidified on a transducer, and hybridized by DNA molecules to identify another DNA containing a complementary sequence to form a stable double-stranded DNA, and the target DNA is subjected to conversion by sound, light, and electric signals. Detection. The principle of DNA biosensor is that a double-stranded DNA formed by hybridization of a single-stranded DNA molecule with a known nucleotide sequence immobilized on the surface of a sensor or transducer probe to another complementary ss-DNA molecule will exhibit a certain The physical signal is finally reflected by the transducer. However, DNA molecules are very small and fragile
Application:
- Environmental: water environment monitoring and atmospheric environment monitoring.
- Military medicine: effective measure against biological weapons, monitor a variety of bacteria, viruses and their toxins, such as Bacillus anthracis, Yersinia pestis.
- Forensic science: DNA identification, paternity testing, etc.
One Example:
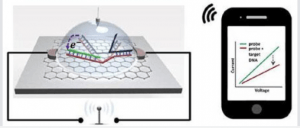
Illustration of graphene-based SNP detection chip wirelessly transmitting signal to a smartphone.
BioSensor chip that can detect a type of genetic mutation known as a single nucleotide polymorphism (SNP) and send the results in real time to an electronic device.
Skill level required for electronics and coding: Expert